
This is a tutorial about writing code in Excel spreadsheets using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
Excel is one of Microsoft’s most popular products. In 2016, the CEO of Microsoft said "Think about a world without Excel. That's just impossible for me.” Well, maybe the world can’t think without Excel.
We’re one big happy family!
In this tutorial, you’ll learn about VBA and how to write code in an Excel spreadsheet using Visual Basic.
You don’t need any prior programming experience to understand this tutorial. However, you will need:
Over the course of this article, you will learn:
Here are some important concepts that you should be familiar with to fully understand this tutorial.
Objects: Excel is object-oriented, which means everything is an object - the Excel window, the workbook, a sheet, a chart, a cell. VBA allows users to manipulate and perform actions with objects in Excel.
If you don’t have any experience with object-oriented programming and this is a brand new concept, take a second to let that sink in!
Procedures: a procedure is a chunk of VBA code, written in the Visual Basic Editor, that accomplishes a task. Sometimes, this is also referred to as a macro (more on macros below). There are two types of procedures:
Note: you can have functions operating inside of subroutines. You’ll see later.
Macros: If you’ve spent any time learning more advanced Excel functionality, you’ve probably encountered the concept of a “macro.” Excel users can record macros, consisting of user commands/keystrokes/clicks, and play them back at lightning speed to accomplish repetitive tasks. Recorded macros generate VBA code, which you can then examine. It’s actually quite fun to record a simple macro and then look at the VBA code.
Please keep in mind that sometimes it may be easier and faster to record a macro rather than hand-code a VBA procedure.
For example, maybe you work in project management. Once a week, you have to turn a raw exported report from your project management system into a beautifully formatted, clean report for leadership. You need to format the names of the over-budget projects in bold red text. You could record the formatting changes as a macro and run that whenever you need to make the change.
Visual Basic for Applications is a programming language developed by Microsoft. Each software program in the Microsoft Office suite is bundled with the VBA language at no extra cost. VBA allows Microsoft Office users to create small programs that operate within Microsoft Office software programs.
Think of VBA like a pizza oven within a restaurant. Excel is the restaurant. The kitchen comes with standard commercial appliances, like large refrigerators, stoves, and regular ole’ ovens - those are all of Excel’s standard features.
But what if you want to make wood-fired pizza? Can’t do that in a standard commercial baking oven. VBA is the pizza oven.

Because wood-fired pizza is the best!
A lot of people spend a lot of time in Excel as a part of their jobs. Time in Excel moves differently, too. Depending on the circumstances, 10 minutes in Excel can feel like eternity if you’re not able to do what you need, or 10 hours can go by very quickly if everything is going great. Which is when you should ask yourself, why on earth am I spending 10 hours in Excel?
Sometimes, those days are inevitable. But if you’re spending 8-10 hours everyday in Excel doing repetitive tasks, repeating a lot of the same processes, trying to clean up after other users of the file, or even updating other files after changes are made to the Excel file, a VBA procedure just might be the solution for you.
You should consider using VBA if you need to:
To write VBA, you’ll need to add the Developer tab to the ribbon, so you’ll see the ribbon like this.
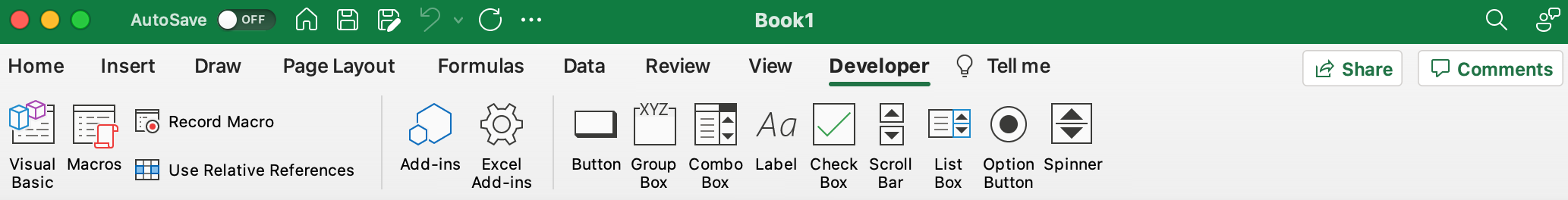
To add the Developer tab to the ribbon:
After you show the tab, the Developer tab stays visible, unless you clear the check box or have to reinstall Excel. For more information, see Microsoft help documentation.
Navigate to the Developer Tab, and click the Visual Basic button. A new window will pop up - this is the Visual Basic Editor. For the purposes of this tutorial, you just need to be familiar with the Project Explorer pane and the Property Properties pane.
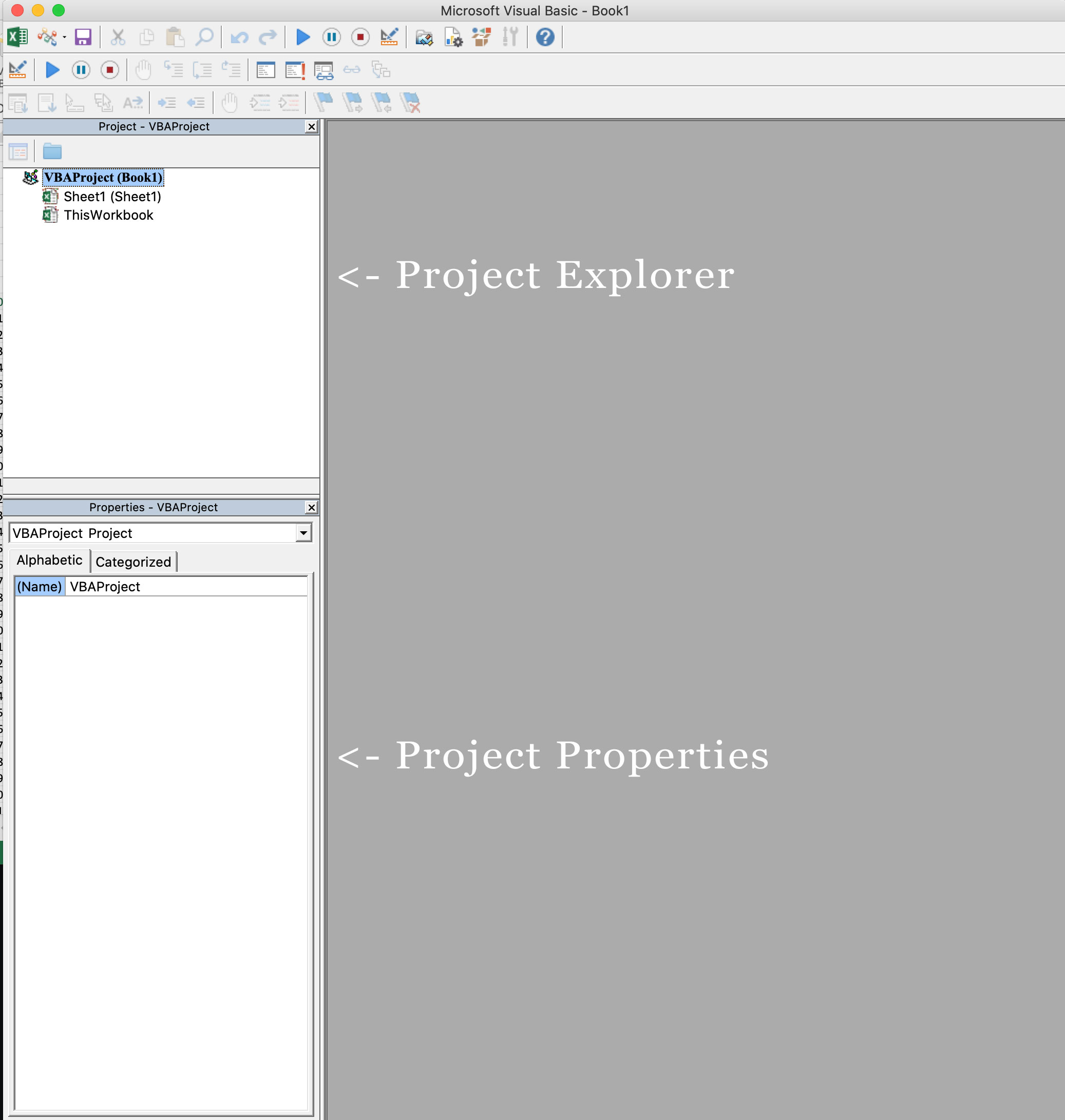
First, let’s create a file for us to play around in.
Let’s rock and roll with some easy examples to get you writing code in a spreadsheet using Visual Basic.
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub Auto_Open() MsgBox ("Welcome to the XYZ Workbook.") End Sub
Save, close the workbook, and reopen the workbook. This dialog should display.

Depending on your familiarity with programming, you may have some guesses. It’s not particularly complex, but there’s quite a lot going on:
In short, this is a simple subroutine that contains a function.
Maybe you have a very important file that is accessed infrequently (say, once a quarter), but automatically updated daily by another VBA procedure. When it is accessed, it’s by many people in multiple departments, all across the company.
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub UserReportQuery() Dim UserInput As Long Dim Answer As Integer UserInput = vbYesNo Answer = MsgBox("Process the XYZ Report?", UserInput) If Answer = vbYes Then ProcessReport End Sub
Sub ProcessReport() MsgBox ("Thanks for processing the XYZ Report.") End Sub
Save and navigate back to the Developer tab of Excel and select the “Button” option. Click on a cell and assign the UserReportQuery macro to the button.
Now click the button. This message should display:

Click “yes” or hit Enter.
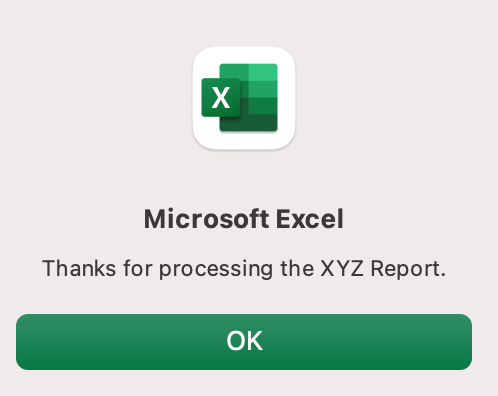
Once again, tada!
Please note that the secondary subroutine, ProcessReport, could be anything. I’ll demonstrate more possibilities in example #3. But first.
This example builds on the previous example and has quite a few new elements. Let’s go over the new stuff:
This could be used in many, many ways. The value and versatility of this functionality is more so defined by what the secondary subroutine does.
For example, maybe you have a file that is used to generate 3 different weekly reports. These reports are formatted in dramatically different ways.
For loops are very useful if you need to perform repetitive tasks on a specific range of values - arrays or cell ranges. In plain English, a loop says “for each x, do y.”
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub LoopExample() Dim X As Integer For X = 1 To 100 Range("A" & X).Value = X Next X End Sub
Save and navigate back to the Developer tab of Excel and select the Macros button. Run the LoopExample macro.
This should happen:
Etc, until the 100th row.
The For-Next loop is one of the most powerful functionalities of VBA; there are numerous potential use cases. This is a more complex example that would require multiple layers of logic, but it communicates the world of possibilities in For-Next loops.
Maybe you have a list of all products sold at your bakery in Column A, the type of product in Column B (cakes, donuts, or muffins), the cost of ingredients in Column C, and the market average cost of each product type in another sheet.
You need to figure out what should be the retail price of each product. You’re thinking it should be the cost of ingredients plus 20%, but also 1.2% under market average if possible. A For-Next loop would allow you to do this type of calculation.
Now that we’ve talked about pizza and muffins and oh-yeah, how to write VBA code in Excel spreadsheets, let’s do a learning check. See if you can answer these questions.
If you have a fair idea of how to you could answer these questions, then this was successful.
Whether you’re an occasional user or a power user, I hope this tutorial provided useful information about what can be accomplished with just a bit of code in your Excel spreadsheets.
I'm Chloe Tucker, an artist and developer in Portland, Oregon. As a former educator, I'm continuously searching for the intersection of learning and teaching, or technology and art. Reach out to me on Twitter @_chloetucker and check out my website at chloe.dev.