Protein Synthesis: Translation
DNA’s biggest process is protein synthesis. This is how the growth and repair of our body occurs. DNA provides a template upon which proteins are coded for. There is some slightly confusing terminology in this section.
Table of Contents
Protein synthesis is the process by which the base sequence found in genes on DNA is used to make polypeptides.
Protein synthesis occurs in two major phases:
- Transcription – during which a strand of mRNA is synthesised from a particular gene template.
- Translation – during which the mRNA attaches to the ribosome, which recruits tRNAs carrying amino acids in order to make a polypeptide.
RNA
RNA is ribonucleic acid – it is similar to DNA but it is single stranded and contains uracil instead of thymine.
An important part of protein synthesis is that the DNA stays in the nucleus. Now if the DNA stays in the nucleus, how does it reach the organelles to allow protein synthesis to occur?
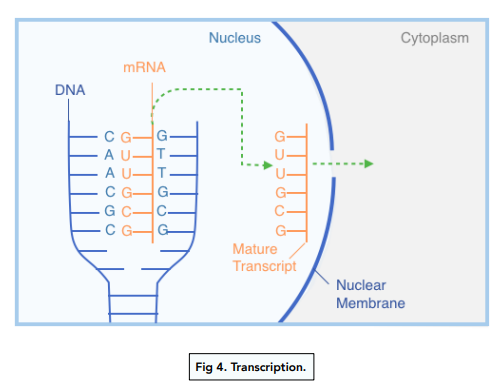
Transcription
- The DNA molecule is unzipped around the gene. DNA is a double stranded molecule so it needs to be unzipped to expose one strand.
- RNA polymerase helps make a copy of DNA as mRNA. RNA polymerase binds to the non-coding region in front of a gene on one of the DNA strands and uses free nucleotides to produce a complementary mRNA (messenger RNA) strand of the coding part of the gene. The copying of the DNA is known as transcription.
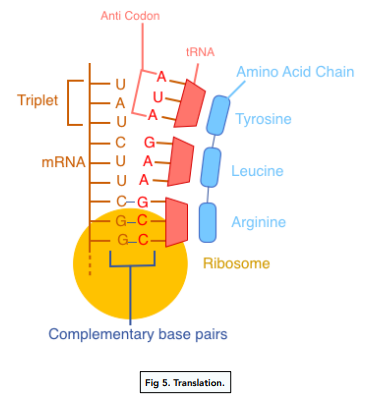
Translation
- mRNA leaves the nucleus, moves into the cytoplasm and attaches to the ribosome. The ribosome is the organelle responsible for protein synthesis.
- tRNA molecules complementary to the mRNA arrive at the ribosome. When the mRNA moves to the ribosome, it recruits tRNA (transfer RNA structures) that are complementary to the base sequence of the mRNA. The tRNA has an anti-codon that is complementary to the mRNA’s codon (sequence of 3 bases).
- The tRNA molecule carry amino acids with it. The bases on the mRNA are read in threes and code for a specific amino acid (the triplet code). The amino acids then bond with another and polypeptides are formed. This is translation.

GCSE Biology Online Course
Covering every topic in the GCSE syllabus
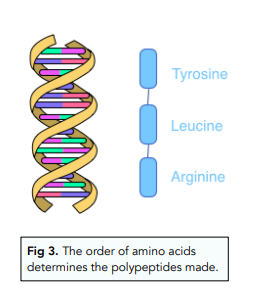
DNA Base Order and Protein Structure
This therefore means that the order of the bases in the DNA determines what amino acids are recruited and what polypeptides are made. Therefore, the structure of the DNA influences what protein is made.
Protein Shape and Enzymes
Once these protein chains are formed, they are folded in a few ways, so each protein has its own unique shape for example, enzymes, antibodies, receptors, neurotransmitters etc. The unique shape is imperative for enzymes, as they have their own individual active sites. These active sites must be individual to each enzyme as they must have a complementary shape to their substrate, to ensure the functionality of the enzyme.
Get Access to 20 Free GCSE Tutorials
Gene Expression and Proteins
The expression of proteins can be altered by switching genes on and off. Now how does this occur?
- DNA is separated into coding and non-coding DNA. The DNA that is coding is what directly determines the proteins formed as a copy of it is made. Non-coding DNA on the other hand has a different function. It works to turn on and off genes. Therefore, if it decides to turn off a section of coding DNA, the protein produced would be different. This can lead to differences in the appearance of the expression of the gene.
- As every cell contains all of the DNA in the body, genes must be switched on and off in order to stop every cell producing every protein. Therefore, different cells have different genes turned on and off
→What is DNA and what does it do?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, and it is the blueprint that contains the instructions for building proteins in our cells. It determines our genetic makeup and helps our bodies function properly.
→What is protein synthesis and why is it important?
Protein synthesis is the process of creating proteins from the instructions in DNA. Proteins are essential for many processes in our bodies, including growth and repair, so protein synthesis is crucial for our overall health.
→What is translation in protein synthesis?
Translation is the second step of protein synthesis, where the instructions in the DNA code are translated into a protein molecule. This is done by ribosomes in the cell, using the genetic code and a molecule called messenger RNA.
→What is messenger RNA and how does it help in translation?
Messenger RNA is a molecule that carries the instructions from the DNA to the ribosomes, where it helps the ribosomes read the code and build the protein.
→What is the genetic code and how does it work in translation?
The genetic code is a set of instructions that tells the ribosomes which amino acids to use to build a protein. It is made up of codons, which are sequences of three nucleotides (building blocks of DNA) that specify a particular amino acid. The ribosomes use this code to match the messenger RNA to the right amino acids and build the protein.
→What role do ribosomes play in translation?
Ribosomes are the “workstations” of the cell where proteins are synthesized. They use the information in the messenger RNA to build the protein, matching codons to the right amino acids and linking them together in the correct order.
→How does translation ensure the accuracy of protein synthesis?
Translation is carefully regulated to make sure that the right amino acids are used in the right order to build the protein correctly. Any mistakes in the genetic code can cause problems with the protein and potentially lead to health problems.
→Can translation go wrong?
Yes, there are several ways that translation can go wrong, such as mutations in the DNA code or problems with the ribosomes. These errors can result in the creation of non-functional or harmful proteins, which can cause health problems.
Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment
Cancel reply
AQA 1. Cell biology
AQA 2. Organisation
AQA 3. Infection and response
AQA 4. Bioenergetics
Food Security – Sustainable Fisheries (GCSE Biology)
Biotechnology – Biotechnology & GM Foods (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Farming Techniques (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Food Production & Security (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Mainatining Bioversity (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Deforestation (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Land Use & Destruction of Peat Bogs (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Pollution and Global Warming (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – Human Population & Increasing Waste (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – (GCSE Biology)
AQA 5. Homeostasis and response
Types of Diseases – Fungal and Protist Diseases (GCSE Biology)
AQA 6. Inheritance, variation and evolution
AQA 7. Ecology
AQA 8. Key ideas
CIE IGCSE 1 Characteristics and classification of living organisms
Classification – (GCSE Biology)
Exercise & Metabolism – Metabolism (GCSE Biology)
Aerobic Respiration – (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 10 Diseases and immunity
Disease Prevention – Human Disease Prevention Systems (GCSE Biology)
The Immune System – Memory of the Immune System (GCSE Biology)
The Immune System – Vaccination (GCSE Biology)
The Immune System – The Role of Antibodies and Antitoxins – (GCSE Biology)
The Immune System – The Immune System and Phagocytosis (GCSE Biology)
Pathogens, Disease and Transmission – Preventing Transmission of Disease (GCSE Biology)
Pathogens, Disease and Transmission – Transmission of Disease (GCSE Biology)
Pathogens, Disease and Transmission – Pathogens Leading to Disease (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 11 Gas exchange in humans
The Lungs – (GCSE Biology)
Exchange Surfaces – Exchange Surfaces: Increasing their Effectiveness (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 12 Respiration
Exercise & Metabolism – Bodily Responses to Exercise (GCSE Biology)
Anaerobic Respiration – Plants and Fungi (GCSE Biology)
Anaerobic Respiration – Animals (GCSE Biology)
Aerobic Respiration – (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 13 Excretion in humans
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Kidney Transplantation (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Kidney Failure and Dialysis (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – The Kidneys and Excretion (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Osmoregulation (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 14 Coordination and response
Plant Hormones – Commercial Use of Plant Hormones (GCSE Biology)
Plant Hormones – Experiments on Plant Responses (GCSE Biology)
Plant Hormones – Tropisms: Phototropism & Geotropism (GCSE Biology)
Control of Blood Glucose Concentration – Diabetes Mellitus: Type I & II (GCSE Biology)
Control of Blood Glucose Concentration – Increasing and Decreasing Blood Glucose Levels (GCSE Biology)
Control of Blood Glucose Concentration – Blood Glucose Homeostasis (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – Increasing and Decreasing Body Temperature (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – Thermoregulation (GCSE Biology)
Human Endocrine System – Hormones: Adrenaline and Thyroxine (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 15 Drugs
Antibiotics – Drug Resistance, Antivirals and Antiseptics (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Drugs: Antibiotics and Painkillers (GCSE Biology)
Lifestyle & Disease – Effects of Smoking and Alcohol on Health (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 16 Reproduction
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – Sexual Reproduction: Pros and Cons (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – Asexual Reproduction: Pros and Cons (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – (GCSE Biology)
Treating Infertility – IVF: Development and Treatment Issues (GCSE Biology)
Treating Infertility – Drugs, IVF and AI for Infertility (GCSE Biology)
Contraception – Hormonal Contraception: The Pill, Patches & Implants (GCSE Biology)
Contraception – Contraception and Non-Hormonal Contraception (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – The Menstrual Cycle: Graphs (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – The Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal Interactions (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – The Menstrual Cycle: Hormones (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 17 Inheritance
Meiosis – Mitosis and Meiosis (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Sex Determination (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Genetic Diagrams (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Genes and Inheritance (GCSE Biology)
DNA – Protein Synthesis: Translation (GCSE Biology)
DNA – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
Cell Division – Stem Cell Types (GCSE Biology)
Cell Division – The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (GCSE Biology)
Cell Division – Nucleus and Chromosomes (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 18 Variation and selection
Ecosystems – Extremophiles (GCSE Biology)
Ecosystems – Adaptations (GCSE Biology)
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Evidence for Evolution: Resistant Bacteria (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Selective Breeding (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Evolution and Natural Selection (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Variation and Its Causes (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Inherited Disorders (GCSE Biology)
DNA – Mutations (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 19 Organisms and their environment
REARRANGED ORDER – Deforestation (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Pollution and Global Warming (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – Human Population & Increasing Waste (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – Decomposition & The Nitrogen Cycle (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – The Water Cycle (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – Cycles & The Carbon Cycle (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Transfer of Biomass (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Pyramids of Biomass (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Trophic Levels & Food Chains (GCSE Biology)
Ecosystems – Biotic Factors (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 2 Organisation of the organism
Transport in Plants – How Plants are Adapted for Photosynthesis (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Cell Organisation (GCSE Biology)
Microscopes & Cultures – Cell Size and Area Estimations (GCSE Biology)
Microscopes & Cultures – Magnification and Unit Conversions (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Specialised Cells: More Cells (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Specialised Cells: Sperm Cells (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Animal and Plant Cells (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 20 Biotechnology and genetic engineering
Biotechnology – Biotechnology & GM Foods (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Genetic Engineering (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 21 Human influences on ecosystems
Food Security – Sustainable Fisheries (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Farming Techniques (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Food Production & Security (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Mainatining Bioversity (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Deforestation (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Land Use & Destruction of Peat Bogs (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Pollution and Global Warming (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 3 Movement in and out of cells
Simple Molecular Covalent Structures (GCSE Chemistry)
Exchange Surfaces – Surface Areas to Volume Ratios (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Diffusion – (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Active Transport (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Measuring the Effects of Osmosis (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Osmosis (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Factors that Affect the Rate of Diffusion (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 4 Biological molecules
DNA – Its Structure (GCSE Biology)
DNA – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Protein and Lipids: Breakdown (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Carbohydrates: Breakdown and Synthesis (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 5 Enzymes
Enzymes & Digestion – Enzyme Action: Factors that Affect it (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Enzymes: An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 6 Plant nutrition
Plant Disease & Defence – Plant Diseases and Deficiencies (GCSE Biology)
Photosynthesis: Greenhouses – (GCSE Biology)
Photosynthesis: Limiting Factors Affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis – (GCSE Biology)
Photosynthesis: An Introduction – (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Plants – How Plants are Adapted for Photosynthesis (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Plants – Structure of a Plant (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 7 Human nutrition
Types of Diseases – Bacterial Diseases: Cholera and Tuberculosis – (GCSE Biology)
Lifestyle & Disease – Diet and Exercise (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – The Digestive System (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Protein and Lipids: Breakdown (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Carbohydrates: Breakdown and Synthesis (GCSE Biology)
Exchange Surfaces – Exchange Surfaces: Increasing their Effectiveness (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 8 Transport in plants
Transpiration – Plant Water Loss (GCSE Biology)
Transpiration – Transpiration Rates (GCSE Biology)
Transpiration – Transpiration in Plants (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Plants – Structure of a Plant (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Plants – Transport Systems in Plants (GCSE Biology)
Exchange Surfaces – Exchange Surfaces: Increasing their Effectiveness (GCSE Biology)
CIE IGCSE 9 Transport in animals
Cardiovascular Disease: Prophylactic Treatment (GCSE Biology)
Cardiovascular Disease: Artificial Hearts and Transplants (GCSE Biology)
Cardiovascular Disease: Stents and Lifestyle (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels: Veins and Capillaries (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels – White Blood Cells and Platelets (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels – Plasma and Red Blood Cells (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels – Arteries (GCSE Biology)
The Circulatory System – Heart: Structure and Function (GCSE Biology)
Circulatory System – The Double Circulatory System (GCSE Biology)
Circulatory System – The Single Circulatory System (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 1 - Key concepts in biology
Exercise & Metabolism – Metabolism (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Enzyme Action: Factors that Affect it (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Enzyme Action: Reaction Rates (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Carbohydrates: Breakdown and Synthesis (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Protein and Lipids: Breakdown (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Enzymes: An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Diffusion – (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Active Transport (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Measuring the Effects of Osmosis (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Osmosis (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 2 - Cells and control
Meiosis – Mitosis and Meiosis (GCSE Biology)
The Eye – The Eye: Its Responses – (GCSE Biology)
The Eye – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
The Brain – Treatments and Challenges (GCSE Biology)
The Brain – Electrical Stimulation and Scans (GCSE Biology)
The Brain – Structures of the Brain (GCSE Biology)
Synapses & Reflexes – Reflexes and the Reflex Arc (GCSE Biology)
Synapses & Reflexes – Synapses (GCSE Biology)
Structure & Function of Nervous System – Structures of the Nervous System (GCSE Biology)
Structure & Function of Nervous System – Functions of the Nervous System (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 3 - Genetics
Variation – The Human Genome Project (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Variation and Its Causes (GCSE Biology)
Meiosis – Mitosis and Meiosis (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Experiments by Mendel (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Sex Determination (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Genetic Diagrams (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Genes and Inheritance (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – Sexual Reproduction: Pros and Cons (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – Asexual Reproduction: Pros and Cons (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 4 - Natural selection and genetic modification
Biotechnology – Biotechnology & GM Foods (GCSE Biology)
Classification – (GCSE Biology)
Fossils & Extinction – Evidence for Evolution: Fossils (GCSE Biology)
Fossils & Extinction – Fossil Formation (GCSE Biology)
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Evidence for Evolution: Resistant Bacteria (GCSE Biology)
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Theory of Speciation (GCSE Biology)
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Theory of Evolution: Darwin and Lamarck (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Cloning (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Genetic Engineering (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Selective Breeding (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 5 - Health, disease and the development of medicines
Plant Disease & Defence – Chemical and Mechanical Plant Defences – (GCSE Biology)
Plant Disease & Defence – Physical Plant Defences (GCSE Biology)
Plant Disease & Defence – Identifying Plant Diseases (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Monoclonal Antibodies in Disease Treatment and Research (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Monoclonal Antibodies in Pregnancy Tests (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Producing Monoclonal Antibodies (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Developing Drugs: Trials and Placebos (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Developing Drugs: Discovery and Development (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Drug Resistance, Antivirals and Antiseptics (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Drugs: Antibiotics and Painkillers (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 6 - Plant structures and their functions
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Trophic Levels & Food Chains (GCSE Biology)
Plant Hormones – Commercial Use of Plant Hormones (GCSE Biology)
Plant Hormones – Tropisms: Phototropism & Geotropism (GCSE Biology)
Photosynthesis: The Inverse Square Law – (GCSE Biology)
Photosynthesis: Limiting Factors Affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis – (GCSE Biology)
Photosynthesis: An Introduction – (GCSE Biology)
Transpiration – Plant Water Loss (GCSE Biology)
Transpiration – Transpiration Rates (GCSE Biology)
Transpiration – Transpiration in Plants (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Plants – How Plants are Adapted for Photosynthesis (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 7 - Animal coordination, control and homeostasis
Treating Infertility – IVF: Development and Treatment Issues (GCSE Biology)
Treating Infertility – Drugs, IVF and AI for Infertility (GCSE Biology)
Contraception – Hormonal Contraception: The Pill, Patches & Implants (GCSE Biology)
Contraception – Contraception and Non-Hormonal Contraception (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – The Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal Interactions (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – The Menstrual Cycle: Hormones (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – Puberty and Hormones (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Kidney Transplantation (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Kidney Failure and Dialysis (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Anti-Diuretic Hormone (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 8 - Exchange and transport in animals
Exercise & Metabolism – Bodily Responses to Exercise (GCSE Biology)
Anaerobic Respiration – Animals (GCSE Biology)
Aerobic Respiration – (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels: Veins and Capillaries (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels – White Blood Cells and Platelets (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels – Plasma and Red Blood Cells (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels – Arteries (GCSE Biology)
The Circulatory System – Heart: Structure and Function (GCSE Biology)
Circulatory System – The Double Circulatory System (GCSE Biology)
The Lungs – (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel 9 - Ecosystems and material cycles
Food Security – Sustainable Fisheries (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Farming Techniques (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Food Production & Security (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Mainatining Bioversity (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Deforestation (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Land Use & Destruction of Peat Bogs (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Pollution and Global Warming (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – Human Population & Increasing Waste (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – The Impact of Environmental Change (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel IGCSE 1 - The nature and variety of living organisms
Types of Diseases – Viral Diseases: HIV (GCSE Biology)
Types of Diseases – Sexually Transmitted Infections (GCSE Biology)
Types of Diseases – Viral Diseases:TMV, Measles and Ebola (GCSE Biology)
Types of Diseases – Fungal and Protist Diseases (GCSE Biology)
Pathogens, Disease and Transmission – Pathogens Leading to Disease (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Bacterial Cells (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Animal and Plant Cells (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel IGCSE 2 - Structure and functions in living organisms
Plant Hormones – Tropisms: Phototropism & Geotropism (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – Puberty and Hormones (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Anti-Diuretic Hormone (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – The Kidneys and Excretion (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Osmoregulation (GCSE Biology)
Control of Blood Glucose Concentration – Increasing and Decreasing Blood Glucose Levels (GCSE Biology)
Control of Blood Glucose Concentration – Blood Glucose Homeostasis (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – Increasing and Decreasing Body Temperature (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – Thermoregulation (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel IGCSE 3 - Reproduction and inheritance
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Evidence for Evolution: Resistant Bacteria (GCSE Biology)
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Theory of Evolution: Darwin and Lamarck (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Evolution and Natural Selection (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Variation and Its Causes (GCSE Biology)
Meiosis – Mitosis and Meiosis (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Sex Determination (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Genetic Diagrams (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Genes and Inheritance (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – (GCSE Biology)
DNA – Mutations (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel IGCSE 4 - Ecology and the environment
REARRANGED ORDER – Deforestation (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Pollution and Global Warming (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – Decomposition & The Nitrogen Cycle (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – Cycles & The Carbon Cycle (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Transfer of Biomass (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Pyramids of Biomass (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Quadrat and Transect Sampling (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Trophic Levels & Food Chains (GCSE Biology)
Ecosystems – Biotic Factors (GCSE Biology)
Edexcel IGCSE 5 - Use of biological resources
Food Security – Sustainable Fisheries (GCSE Biology)
Biotechnology – Biotechnology & GM Foods (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Farming Techniques (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Food Production & Security (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Cloning (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Genetic Engineering (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Selective Breeding (GCSE Biology)
OCR B1.1 Cell structures
Cell Division – Nucleus and Chromosomes (GCSE Biology)
Microscopes & Cultures – Magnification and Unit Conversions (GCSE Biology)
Microscopes & Cultures – Microscopes (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Animal and Plant Cells (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes (GCSE Biology)
OCR B1.2 What happens in cells (and what do cells need)?
DNA – Protein Synthesis: Translation (GCSE Biology)
DNA – Its Structure (GCSE Biology)
DNA – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
Exercise & Metabolism – Metabolism (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Enzyme Action: Reaction Rates (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Enzyme Action: Factors that Affect it (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Enzymes: An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
OCR B1.3 Respiration
Anaerobic Respiration – Plants and Fungi (GCSE Biology)
Anaerobic Respiration – Animals (GCSE Biology)
Aerobic Respiration – (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Protein and Lipids: Breakdown (GCSE Biology)
Enzymes & Digestion – Carbohydrates: Breakdown and Synthesis (GCSE Biology)
OCR B1.4 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis: The Inverse Square Law – (GCSE Biology)
Photosynthesis: Limiting Factors Affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis – (GCSE Biology)
Photosynthesis: An Introduction – (GCSE Biology)
OCR B2.1 Supplying the cell
Transport in Cells – Diffusion – (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Active Transport (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Measuring the Effects of Osmosis (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Cells – Osmosis (GCSE Biology)
Cell Division – Stem Cell Types (GCSE Biology)
Cell Division – Mitosis: its Stages (GCSE Biology)
Cell Division – The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Cell Differentiation (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Specialised Cells: More Cells (GCSE Biology)
Introduction to Cells – Specialised Cells: Sperm Cells (GCSE Biology)
OCR B2.2 The challenges of size
Transpiration – Plant Water Loss (GCSE Biology)
Transpiration – Transpiration Rates (GCSE Biology)
Transpiration – Transpiration in Plants (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Plants – Structure of a Plant (GCSE Biology)
Transport in Plants – Transport Systems in Plants (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels: Veins and Capillaries (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels – Plasma and Red Blood Cells (GCSE Biology)
Blood and Blood Vessels – Arteries (GCSE Biology)
The Circulatory System – Heart: Structure and Function (GCSE Biology)
Circulatory System – The Double Circulatory System (GCSE Biology)
OCR B3.1 Coordination and control – the nervous system
The Eye – The Eye: Its Responses – (GCSE Biology)
The Eye – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
The Brain – Treatments and Challenges (GCSE Biology)
The Brain – Electrical Stimulation and Scans (GCSE Biology)
The Brain – Structures of the Brain (GCSE Biology)
Synapses & Reflexes – Reflexes and the Reflex Arc (GCSE Biology)
Structure & Function of Nervous System – Structures of the Nervous System (GCSE Biology)
Structure & Function of Nervous System – Functions of the Nervous System (GCSE Biology)
OCR B3.2 Coordination and control – the endocrine system
Plant Hormones – Commercial Use of Plant Hormones (GCSE Biology)
Plant Hormones – Experiments on Plant Responses (GCSE Biology)
Plant Hormones – Tropisms: Phototropism & Geotropism (GCSE Biology)
Treating Infertility – IVF: Development and Treatment Issues (GCSE Biology)
Treating Infertility – Drugs, IVF and AI for Infertility (GCSE Biology)
Contraception – Hormonal Contraception: The Pill, Patches & Implants (GCSE Biology)
Contraception – Contraception and Non-Hormonal Contraception (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – The Menstrual Cycle: Graphs (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – The Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal Interactions (GCSE Biology)
Hormones in Human Reproduction – The Menstrual Cycle: Hormones (GCSE Biology)
OCR B3.3 Maintaining internal environments Topic
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Anti-Diuretic Hormone (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – The Kidneys and Excretion (GCSE Biology)
Osmoregulation & The Kidney – Osmoregulation (GCSE Biology)
Control of Blood Glucose Concentration – Diabetes Mellitus: Type I & II (GCSE Biology)
Control of Blood Glucose Concentration – Increasing and Decreasing Blood Glucose Levels (GCSE Biology)
Control of Blood Glucose Concentration – Blood Glucose Homeostasis (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – Increasing and Decreasing Body Temperature (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
Homeostasis – Thermoregulation (GCSE Biology)
OCR B4.1 Ecosystems
Cycles – Decomposition & The Nitrogen Cycle (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – The Water Cycle (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – Cycles & The Carbon Cycle (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Transfer of Biomass (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Pyramids of Biomass (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Quadrat and Transect Sampling (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Trophic Levels & Food Chains (GCSE Biology)
Ecosystems – Biotic Factors (GCSE Biology)
Ecosystems – Abiotic Factors (GCSE Biology)
Ecosystems – Ecosystems and Communities (GCSE Biology)
OCR B5.1 Inheritance
Variation – Variation and Its Causes (GCSE Biology)
Meiosis – Mitosis and Meiosis (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Experiments by Mendel (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Sex Determination (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Genetic Diagrams (GCSE Biology)
Inheritance – Genes and Inheritance (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – Sexual Reproduction: Pros and Cons (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – Asexual Reproduction: Pros and Cons (GCSE Biology)
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction – (GCSE Biology)
DNA – An Introduction (GCSE Biology)
OCR B5.2 Natural selection and evolution
REARRANGED ORDER – Mainatining Bioversity (GCSE Biology)
Classification – (GCSE Biology)
Fossils & Extinction – Extinctinction (GCSE Biology)
Fossils & Extinction – Evidence for Evolution: Fossils (GCSE Biology)
Fossils & Extinction – Fossil Formation (GCSE Biology)
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Evidence for Evolution: Resistant Bacteria (GCSE Biology)
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Theory of Speciation (GCSE Biology)
Development and Understanding of Evolution – Theory of Evolution: Darwin and Lamarck (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Evolution and Natural Selection (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Variation and Its Causes (GCSE Biology)
OCR B6.1 Monitoring and maintaining the environment
REARRANGED ORDER – Mainatining Bioversity (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Deforestation (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Land Use & Destruction of Peat Bogs (GCSE Biology)
REARRANGED ORDER – Pollution and Global Warming (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – Human Population & Increasing Waste (GCSE Biology)
Biodiversity – (GCSE Biology)
Cycles – The Impact of Environmental Change (GCSE Biology)
Organisation & Trophic Levels – Quadrat and Transect Sampling (GCSE Biology)
OCR B6.2 Feeding the human race
Biotechnology – Biotechnology & GM Foods (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Farming Techniques (GCSE Biology)
Food Security – Food Production & Security (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Genetic Engineering (GCSE Biology)
Variation – Selective Breeding (GCSE Biology)
OCR B6.3 Monitoring and maintaining health
Variation – Genetic Engineering (GCSE Biology)
Variation – The Human Genome Project (GCSE Biology)
Plant Disease & Defence – Plant Diseases and Deficiencies (GCSE Biology)
Plant Disease & Defence – Chemical and Mechanical Plant Defences – (GCSE Biology)
Plant Disease & Defence – Physical Plant Defences (GCSE Biology)
Plant Disease & Defence – Identifying Plant Diseases (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Monoclonal Antibodies in Disease Treatment and Research (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Monoclonal Antibodies in Pregnancy Tests (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Producing Monoclonal Antibodies (GCSE Biology)
Antibiotics – Developing Drugs: Trials and Placebos (GCSE Biology)
Related links
Boost your GCSE Biology Performance
GCSE Biology Tutors
Get a 9 in GCSE Biology with our Trusted 1-1 Tutors. Enquire now.
GCSE Biology Online Course
100+ Video Tutorials, Flashcards and Weekly Seminars. 100% Money Back Guarantee
Biology Summer School
Gain hands-on experience of how physics is used in different fields. Boost your university application with our summer programme!
GCSE Biology Weekly Classes
Learn live with other students and gain expert tips and advice to boost your score.
Cookies on Study Mind
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Functional Functional Always active
The technical storage or access is strictly necessary for the legitimate purpose of enabling the use of a specific service explicitly requested by the subscriber or user, or for the sole purpose of carrying out the transmission of a communication over an electronic communications network.
Preferences Preferences
The technical storage or access is necessary for the legitimate purpose of storing preferences that are not requested by the subscriber or user.
Statistics Statistics
The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for statistical purposes. The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for anonymous statistical purposes. Without a subpoena, voluntary compliance on the part of your Internet Service Provider, or additional records from a third party, information stored or retrieved for this purpose alone cannot usually be used to identify you.
Marketing Marketing
The technical storage or access is required to create user profiles to send advertising, or to track the user on a website or across several websites for similar marketing purposes.





